3D scanning is the process of digitising objects by getting the information about its shape and texture. The wall between physical objects in the real world and the digital design environment has been torn down with the help of 3d scanning and 3d printing.
With 3D Scanning, the technical drawings or blueprints of the existing product can be stored, shared or modified for future reference or manufacturing. There are lot of benefits of 3d scanning or reverse engineering:
- With 3D scanning and prototyping technology, newly designed product can be launched to market faster.
- 3D scanning and dedicated softwares gives a better understanding about the performance of the product.
- Convenience and flexibility of 3d scanning for a wide variety of applications, including every aspect of the product life cycle.
- With the help of automation, the technology can be spread beyond the specialist into main stream engineering.
- With 3d scanning we can achieve greater accuracy, speed and reliability for mission-critical projects as compared to other inspection methods.
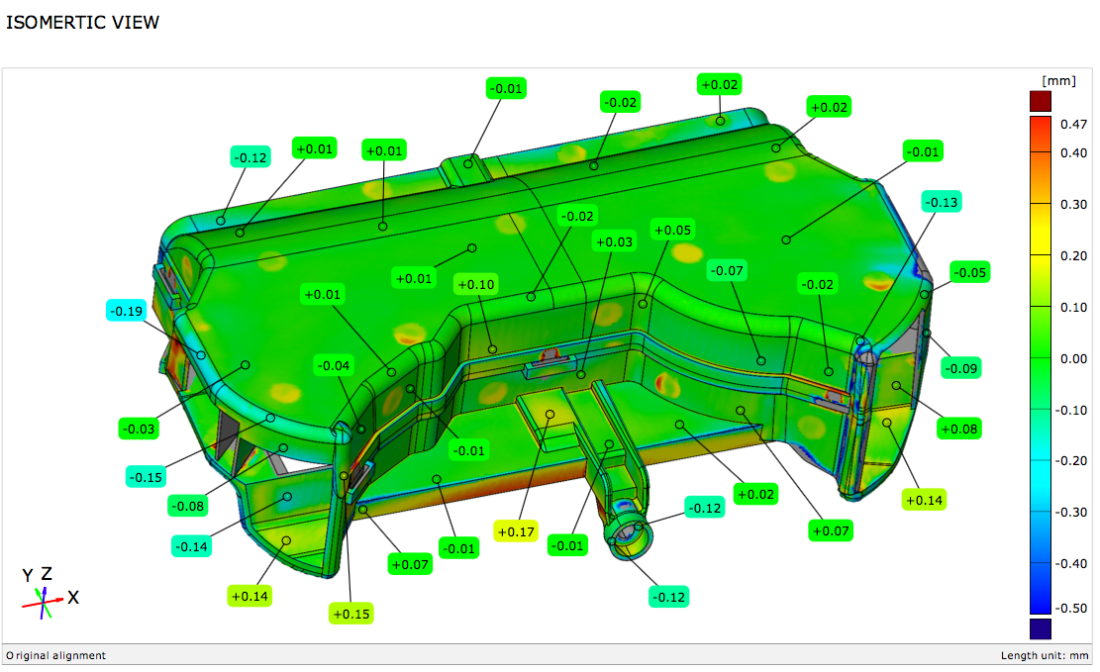
The most important and widely used application of 3D Scanning is in performing Deviation analysis and Quality Inspection.
The method of inspection of 3D Scan of an product in comparison to its CAD data or other scan data is known as Deviation Analysis. The process is also called as Computer-Aided Verification (CAV) or Computer-Aided Inspection (CAI).
In statistics, deviation analysis is a measurement of the absolute difference between any one number in a set and the mean of the set.
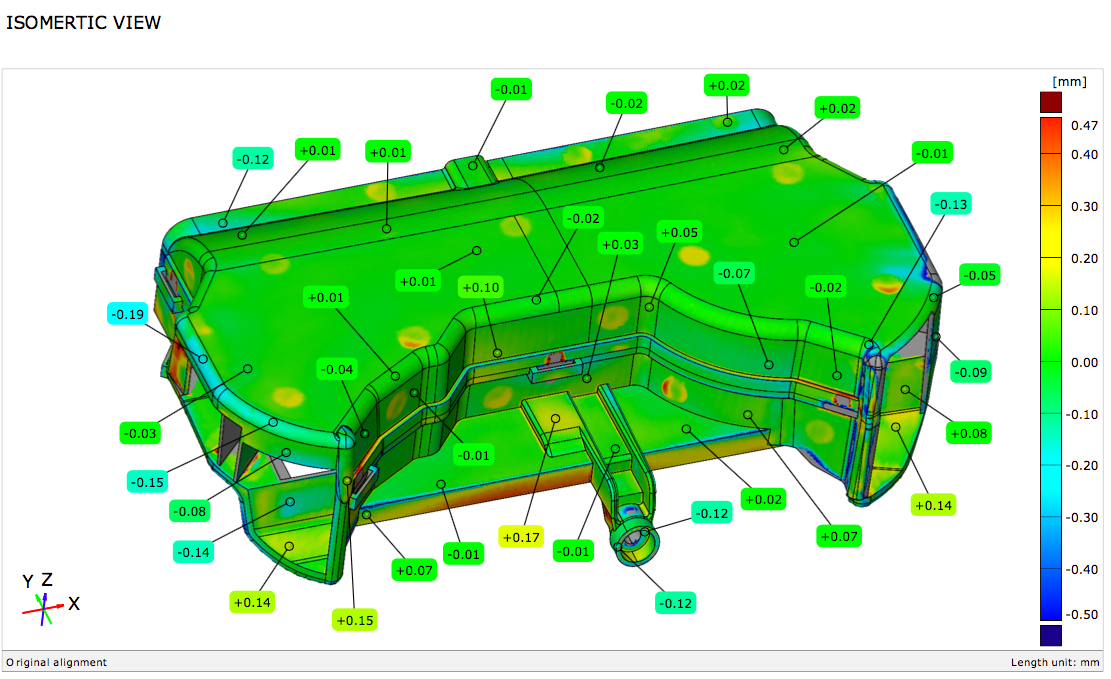
Deviation analysis is a proven method for checking the quality and accuracy of various physical objects, from small mechanical parts to very large structures; from cars to aeroplanes; and nearly anything else that requires precision manufacturing.
When deviation analysis is used for inspection applications, 3D scan data is captured using a 3D scanner. Then the 3d scanned data may be compared to existing CAD drawings or to previously scanned scan data. Deviation Analysis method is extremely cost-effective way to capture near full-coverage of any part and compare it to a known standard. Colour maps are used to visually identify sink, warp, twist and other undesirable characteristics as you evaluate your parts or tools. This is especially useful for organic and complex shapes where traditional CMM inspection may lack coverage and point density.
For 3D scanning services or deviation analysis service projects in your region, contact Designifying at +91-9999-36-3927 or hello@designifying.com